You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Fellows our “raw no pull out” motto has fallen on deaf ears!!!! Birth rates, world wide are disturbingly low!!!!
- Thread starter Mask
- Start date
cuz sometimes the nut oozes outta their asshole into the pussy.......da fuq zod got to do with this??? since when does ass fuckin get bitches pregnant???



i dont know if you want babies from that...cuz sometimes the nut oozes outta their asshole into the pussy.......



Shit, I'm single and decent with my money and life is just to fuckin expensive. ....and that's not just now; been that way my whole adult life. I've always wondered how my parents did it(two kids) on their salaries and how my friends are doing it.
Took me a long time, but I'm making what is for me, some decent $$$, and I still can't imagine being able to raise one, let alone more than one kid without being broke. Shout out to you all that have been able to do it.
.
.
Took me a long time, but I'm making what is for me, some decent $$$, and I still can't imagine being able to raise one, let alone more than one kid without being broke. Shout out to you all that have been able to do it.
.
.
cuz sometimes the nut oozes outta their asshole into the pussy.......
i dont know if you want babies from that...









Population control is back firing in the parasitic elites face,
and they are too spiritually retarded to stop it or even notice it,
they think it will preserve their positions when all its doing is speeding
up their demise!!
and they are too spiritually retarded to stop it or even notice it,
they think it will preserve their positions when all its doing is speeding
up their demise!!
That is true, but like I said earlier in this post, I think something biological is going on. To the young people in this world (the few of you that are around) you guys are going to have an interesting future, I wish you luck. Between the low birth rates and climate change earth maybe very hostile to all life in the near futureCan't nobody afford that shit
No, that doesn’t have anything to do with it. As I said a minute ago, there was something biological going on now. But there are some areas of the world in a United States that a woman has little to no support system if she is pregnant or have the child. Conservatives are going to find out the hard way about trying to outlaw abortion.The union between man and woman is the real problem
Raw no pull out..doesn't mean more babies...just more plan b's
In some cases, you could skeet all you want to, but you still cannot produce a baby.Raw no pull out..doesn't mean more babies...just more plan b's
So childsupport should be at an all time low.
That may be.So child support should be at an all time low.
Shit ain’t low in the states LmaoSo childsupport should be at an all time low.
“Serbia has demographically settled at a pretty decent place in comparison with most of its neighbors with a stable fertility rate. The country will likely see ~60,000 births this year & maintain a TFR above 1.6. In the Balkans it is only outperformed by Montenegro & Bulgaria”

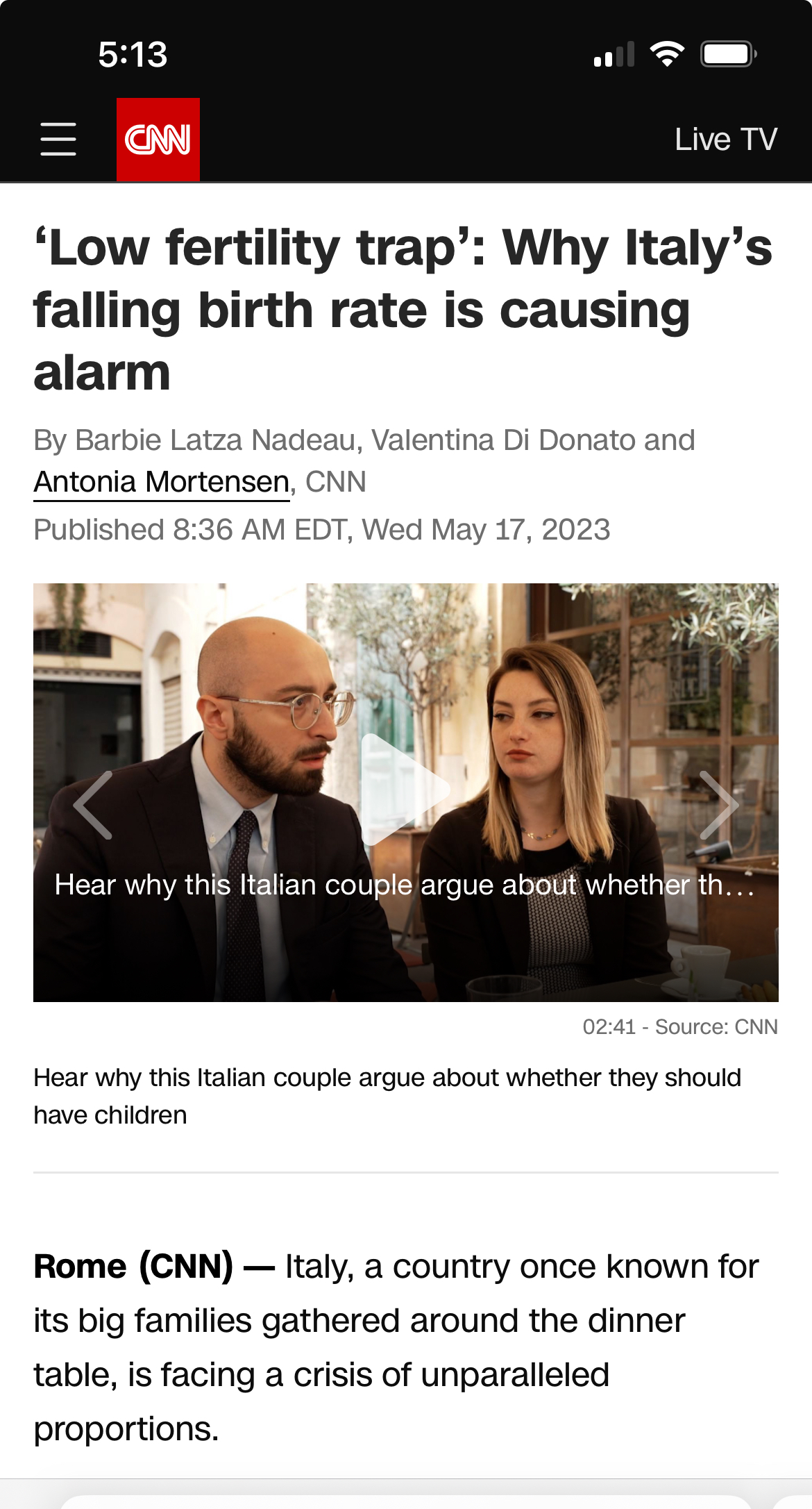
Italy’s birth rate is at a record low. Young Italians say they can’t afford to have babies | CNN
Italy, a country once known for its big families gathered around the dinner table, is facing a crisis of unparalleled proportions.amp.cnn.com
From my recent travels, Europe is a truly a nursing home.
That is true, but like I said earlier in this post, I think something biological is going on. To the young people in this world (the few of you that are around) you guys are going to have an interesting future, I wish you luck. Between the low birth rates and climate change earth maybe very hostile to all life in the near future
Human Penises Are Getting Bigger At A Fast Rate, But That Might Not Be A Good Thing
Abstract
Purpose
Normative male genital measurements are clinically useful and temporal changes would have important implications. The aim of the present study is to characterize the trend of worldwide penile length over time.Materials and Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis using papers from PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library from inception to April 2022 was performed. PRISMA guidelines were used for abstracting data and assessing data quality and validity. Pooled means and standard deviations for flaccid, stretched, and erect length were obtained. Subgroup analyses were performed by looking at differences in the region of origin, population type, and the decade of publication. Metaregression analyses were to adjusted for potential confounders.Results
Seventy-five studies published between 1942 and 2021 were evaluated including data from 55,761 men. The pooled mean length estimates were flaccid length: 8.70 cm (95% CI, 8.16–9.23), stretched length: 12.93 cm (95% CI, 12.48–13.39), and erect length: 13.93 cm (95% CI, 13.20–14.65). All measurements showed variation by geographic region. Erect length increased significantly over time (QM=4.49, df=2, p=0.04) in several regions of the world and across all age groups, while no trends were identified in other penile size measurements. After adjusting for geographic region, subject age, and subject population; erect penile length increased 24% over the past 29 years.Conclusions
The average erect penis length has increased over the past three decades across the world. Given the significant implications, attention to potential causes should be investigated.Keywords
Anatomy; Hormones; Meta-analysis; Penis
INTRODUCTION
As male sexual dysfunction diagnoses and treatments are common [1, 2], penile size remains important [3]. Penile size has been suggested to associate with sexual strength, virility, and vitality in men [4], as well as a man’s self-esteem [5].The penis is formed during gestation under hormonal influences and continues to grow through puberty [6]. Investigators have reported changes in normal male genital development over time as assessed by falling sperm counts, declines in serum testosterone levels, higher rates of testicular tumors, and increasing genital birth defects [7, 8, 9, 10]. While the etiology of reported changes is uncertain, many have hypothesized environmental changes as potential culprits [7, 11].
Penile size has been measured in several studies but no comprehensive study exists to examine geographic variation or temporal trend [12, 13, 14]. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to critically evaluate the literature to report the trend of penile length over time and in different geographic regions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Evidence acquisition
The protocol for this systematic review and meta-analysis was registered in PROSPERO (registration number: CRD42022335620). This meta-analysis was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The following research question was established based on the PICO criteria [15]: Has penile length changed over time globally? We performed a systematic review of the literature in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane from inception to April 2022, to identify studies that evaluated penile size. Search terms included: “Penile Length” OR (“Width” OR “Circumference” OR “Dimension”) AND (“Erect” OR “Flaccid” OR “Stretched”). The reference lists of the included studies were also screened for relevant articles. Seventy-five original articles were included and critically evaluated.
2. Selection of the studies and criteria for inclusion
This analysis was restricted to data collected from original articles that examined men’s penile length. Studies were considered eligible if the quantitative measurement of penis size was measured by an investigator, the sample included ≥10 participants, participants were aged ≥17 years, and if they provided sample size, mean, and standard deviation (SD) of flaccid or erect length measured from the root (pubo-penile junction) of the penis to the tip of the glans (meatus) on the dorsal surface. Articles were excluded if they were based on a self-measurement and if they reported measurements done after major pelvic surgery. Abstracts and meeting reports were excluded from the analysis.
Two authors (FB and ME) independently screened the titles and abstracts of all articles. Abstracts and full-text articles were examined independently by five authors (FB, FDG, EM, ME, and FG) to determine whether or not they met the inclusion criteria. Final inclusion was determined by the consensus of all investigators. Selected articles meeting the inclusion criteria were then critically analyzed.
The following data were extracted from the included studies by using a standardized form: country and region of origin, publication year, sample size, participants' age, penile measurements, population description, and measurement technique.
"Erect length increased significantly over time in several regions of the world and across all age groups," the team wrote in the study. "After adjusting for geographic region, subject age, and subject population; erect penile length increased 24 percent over the past 29 years".
That's an increase from 12.3 centimeters (4.8 inches) to 15.2 centimeters (6 inches) in just under three decades.
The authors explained that they had been motivated to compare penis sizes over time because of other changes to men's reproductive health in recent years, such as declining sperm count.
"Given the trends we'd seen in other measures of men's reproductive health, we thought there could be a decline in penile length due to the same environmental exposures," lead author Michael Eisenberg, professor of urology at Stanford Medicine, said in a press release.
That wasn't the case, but Eisenberg believes that the increase seen could be the result of changes to environments.
"There could be a number of factors at play, such as chemical exposure, like pesticides or hygiene products, interacting with our hormonal systems. These endocrine-disrupting chemicals – there are many – exist in our environment and our diet," he said. "As we change our body's constitution that also affects our hormonal milieu. Chemical exposure has also been posited as a cause for boys and girls going into puberty earlier, which can affect genital development."
The team noted that other factors, such as techniques for measuring length, temperature, and arousal state of the participant, could affect the results. However, they believe that it warrants further study, given the implications it could have for male reproductive health.
"The increase happened over a relatively short period of time," Eisenberg added. "If we're seeing this fast of a change, it means that something powerful is happening to our bodies. We should try to confirm these findings and if confirmed, we must determine the cause of these changes."
Sperm Count Has Declined Almost 50% In Men Across The Globe In Recent Decades
Based on a meta-analysis of data from 53 countries across all seven continents, an international collaboration of scientists has shown that sperm counts have continued to decline and even accelerated in some areas, suggesting a worrying downwards trajectory in both fertility and men’s overall health.
According to the study authors, time is running out and the world needs to act fast.
“Our findings serve as a canary in a coal mine,” said Professor Hagai Levine of Hebrew University of Jerusalem’s Hadassah Braun School, in a statement.
“We have a serious problem on our hands that, if not mitigated, could threaten mankind’s survival. We urgently call for global action to promote healthier environments for all species and reduce exposures and behaviors that threaten our reproductive health."
Alarm bells rang during the pandemic over declining sperm quality, and significant attention was brought to it by the misinformation that the COVID-19 vaccine supposedly affected sperm count and quality. In actuality, infection from COVID-19 did have an effect on this but the vaccine did not, though it did draw scrutiny towards declining sperm counts across men.
In a recent study, a team led by Professor Levine trawled through a diverse set of data from 223 different studies that contain sperm quality data from 1973-2018 and across various different continents, but specifically in continents that were not widely studied before, including South America, Asia and Africa. Covariates were accounted for and analysis performed on the data to look for trends across the board.
The study showed that men in these regions showed similar trends to those found in North America, Europe, and Australia, and that after 2000, the decline in sperm count and concentration accelerated.
“Overall, we’re seeing a significant worldwide decline in sperm counts of over 50 percent in the past 46 years, a decline that has accelerated in recent years,” said Levine.
Unfortunately, all we know from the study is that sperm count is declining, but not why. Levine states that is likely due to a cocktail of lifestyle choices, environmental chemicals, and potential disturbances in reproductive tract development before birth. A huge study in China earlier this year revealed that the large amount of air pollution may be wreaking havoc on sperm count, with people that lived in areas of higher pollution having higher rates of sperm decline.
However, further studies will be needed to uncover the full picture about where the world’s sperm is going.
The study was published in Human Reproduction Update.
And this is my point I remember this article from a while ago. This is why I always said that something biological is going on.Sperm Count Has Declined Almost 50% In Men Across The Globe In Recent Decades
Based on a meta-analysis of data from 53 countries across all seven continents, an international collaboration of scientists has shown that sperm counts have continued to decline and even accelerated in some areas, suggesting a worrying downwards trajectory in both fertility and men’s overall health.
According to the study authors, time is running out and the world needs to act fast.
“Our findings serve as a canary in a coal mine,” said Professor Hagai Levine of Hebrew University of Jerusalem’s Hadassah Braun School, in a statement.
“We have a serious problem on our hands that, if not mitigated, could threaten mankind’s survival. We urgently call for global action to promote healthier environments for all species and reduce exposures and behaviors that threaten our reproductive health."
Alarm bells rang during the pandemic over declining sperm quality, and significant attention was brought to it by the misinformation that the COVID-19 vaccine supposedly affected sperm count and quality. In actuality, infection from COVID-19 did have an effect on this but the vaccine did not, though it did draw scrutiny towards declining sperm counts across men.
In a recent study, a team led by Professor Levine trawled through a diverse set of data from 223 different studies that contain sperm quality data from 1973-2018 and across various different continents, but specifically in continents that were not widely studied before, including South America, Asia and Africa. Covariates were accounted for and analysis performed on the data to look for trends across the board.
The study showed that men in these regions showed similar trends to those found in North America, Europe, and Australia, and that after 2000, the decline in sperm count and concentration accelerated.
“Overall, we’re seeing a significant worldwide decline in sperm counts of over 50 percent in the past 46 years, a decline that has accelerated in recent years,” said Levine.
Unfortunately, all we know from the study is that sperm count is declining, but not why. Levine states that is likely due to a cocktail of lifestyle choices, environmental chemicals, and potential disturbances in reproductive tract development before birth. A huge study in China earlier this year revealed that the large amount of air pollution may be wreaking havoc on sperm count, with people that lived in areas of higher pollution having higher rates of sperm decline.
However, further studies will be needed to uncover the full picture about where the world’s sperm is going.
The study was published in Human Reproduction Update.
The ones who’s studying these issues, know who and why this is happening…Sperm Count Has Declined Almost 50% In Men Across The Globe In Recent Decades
Based on a meta-analysis of data from 53 countries across all seven continents, an international collaboration of scientists has shown that sperm counts have continued to decline and even accelerated in some areas, suggesting a worrying downwards trajectory in both fertility and men’s overall health.
According to the study authors, time is running out and the world needs to act fast.
“Our findings serve as a canary in a coal mine,” said Professor Hagai Levine of Hebrew University of Jerusalem’s Hadassah Braun School, in a statement.
“We have a serious problem on our hands that, if not mitigated, could threaten mankind’s survival. We urgently call for global action to promote healthier environments for all species and reduce exposures and behaviors that threaten our reproductive health."
Alarm bells rang during the pandemic over declining sperm quality, and significant attention was brought to it by the misinformation that the COVID-19 vaccine supposedly affected sperm count and quality. In actuality, infection from COVID-19 did have an effect on this but the vaccine did not, though it did draw scrutiny towards declining sperm counts across men.
In a recent study, a team led by Professor Levine trawled through a diverse set of data from 223 different studies that contain sperm quality data from 1973-2018 and across various different continents, but specifically in continents that were not widely studied before, including South America, Asia and Africa. Covariates were accounted for and analysis performed on the data to look for trends across the board.
The study showed that men in these regions showed similar trends to those found in North America, Europe, and Australia, and that after 2000, the decline in sperm count and concentration accelerated.
“Overall, we’re seeing a significant worldwide decline in sperm counts of over 50 percent in the past 46 years, a decline that has accelerated in recent years,” said Levine.
Unfortunately, all we know from the study is that sperm count is declining, but not why. Levine states that is likely due to a cocktail of lifestyle choices, environmental chemicals, and potential disturbances in reproductive tract development before birth. A huge study in China earlier this year revealed that the large amount of air pollution may be wreaking havoc on sperm count, with people that lived in areas of higher pollution having higher rates of sperm decline.
However, further studies will be needed to uncover the full picture about where the world’s sperm is going.
The study was published in Human Reproduction Update.
That’s my thoughts on the situation
Young women dont wanna do what mama and grandma did. They call is slavery
According to the lancet study researchers estimate that by 2050, 155 of 204 (76%) countries+territories will have below replacement fertility. The number of countries and territories below replacement level is predicted to further increase to 198 of 204 (97%) by 2100
Global fertility rate to keep plummeting, major study warns
Wed, 20 March 2024, 6:33 pm GMT-5The fertility rate in half of all nations is already too low to maintain their population size, a new study says (DIBYANGSHU SARKAR)
The population of almost every country will be shrinking by the end of the century, a major study said Wednesday, warning that baby booms in developing nations and busts in rich ones will drive massive social change.
The fertility rate in half of all nations is already too low to maintain their population size, an international team of hundreds of researchers reported in The Lancet.
Using a huge amount of global data on births, deaths and what drives fertility, the researchers tried to forecast the future for the world's population.
By 2050, the population of three quarters of all countries will be shrinking, according to the study by the US-based Institute For Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME).
At the end of the century, that will be true for 97 percent -- or 198 out of 204 countries and territories, the researchers projected.
Only Samoa, Somalia, Tonga, Niger, Chad and Tajikistan are expected to have fertility rates exceeding the replacement level of 2.1 births per female in 2100, the study estimated.
During this century, fertility rates will continue to increase in developing countries, particularly those in sub-Saharan Africa, even as they tumble in wealthier, ageing nations.
"The world will be simultaneously tackling a 'baby boom' in some countries and a 'baby bust' in others," senior study author Stein Emil Vollset of the IHME said in a statement.
- 'Implications are immense' -
"We are facing staggering social change through the 21st century," he said in a statement.
IHME researcher Natalia Bhattacharjee said the "implications are immense".
"These future trends in fertility rates and live births will completely reconfigure the global economy and the international balance of power and will necessitate reorganising societies," she said.
"Once nearly every country's population is shrinking, reliance on open immigration will become necessary to sustain economic growth."
However World Health Organization experts urged caution for the projections.
They pointed out several limitations of the models, particularly a lack of data from many developing nations.
Communication about the figures "should not be sensationalised, but nuanced, balancing between gloom and optimism," the WHO experts wrote in The Lancet.
They also pointed out that there can be benefits of having a smaller population, such as for the environment and food security. But there are disadvantages for labour supply, social security and "nationalistic geopolitics".
Teresa Castro Martin, a researcher at the Spanish National Research Council not involved in the study, also emphasised that these are just projections.
She pointed out that the Lancet study predicts the global fertility rate will fall below replacement levels around 2030, "whereas the UN predicts this to occur around 2050".
The study was an update of the IHME's Global Burden of Disease study. The organisation, set up at the University of Washington by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, has become a global reference for health statistics.
jdy-dl/yad
Damn the EU and y’all want to let France leader convince y’all to go to war 
“It is likely that the fertility rate for the entire 448 million string European Union fell to its lowest level on record (~1.41) in 2023. The economic, cultural, & national security ramifications of this will be absolutely enormous in the decades ahead.”

“It is likely that the fertility rate for the entire 448 million string European Union fell to its lowest level on record (~1.41) in 2023. The economic, cultural, & national security ramifications of this will be absolutely enormous in the decades ahead.”
Australian births fell by 3.5% in the 1st 9 months of 2023. If this trend continued throughout last year TFR could have fallen as low as 1.55. If Australia dropped  1.6 in 2023 that is extremely significant. It follows a trend seen in Canada & the UK.
1.6 in 2023 that is extremely significant. It follows a trend seen in Canada & the UK.
Australia, Canada, & the UK (as well as the United States) have taken in massive number of immigrants without addressing the severe housing shortage. In the first three countries this has not only driven down native TFR but immigrant TFR as well. Canada is 1.3 & the UK
1.3 & the UK  1.5.
1.5.
Australia, Canada, & the UK (as well as the United States) have taken in massive number of immigrants without addressing the severe housing shortage. In the first three countries this has not only driven down native TFR but immigrant TFR as well. Canada is
Canary Islands really are going for the lowest TFR of any region in European recorded history. The TFR of the islands are already at East Asian levels of 0.80 or so. If they were to continue falling by another 10% they will be at the South Korean depths this year.
Really
Alarming
Worldwide birthrate statistics
Alarming
Worldwide birthrate statistics
I think this was media in here
“Social media has caused many very young people to have extremely high social, professional, & living standard expectations and anxiety. For many the disconnect of these expectations with reality was far too much. For others constantly being bombarded with noise drove them over the edge.”
“Social media has caused many very young people to have extremely high social, professional, & living standard expectations and anxiety. For many the disconnect of these expectations with reality was far too much. For others constantly being bombarded with noise drove them over the edge.”
I keep telling you guys something biological is going on. North and South Korea is having major birth issues….. Japan hits 13 year of birth decline….. Europe is seeing a huge decline. Also the elephant in the room with China Real Estate mass is the population is beginning to decline rapidly.
“The Greek government is planning in May 2024 to unveil new measures to boost birthrates. These include cash benefits for families, affordable housing for young people, & financial incentives for assisted reproduction. Such policies have had unimpressive results in other countries.”


